Edge security refers to the protection of company resources that are no longer contained inside the secure confines of a centralized data center. It’s intended to secure data at a company’s network’s furthest reaches, or “edge,” where it can be particularly exposed to security attacks.
What Is Edge Computing?
The delivery of corporate resources is referred to as edge computing. Rather than depending on a centralized data center to store, analyze, and disseminate apps and data, edge computing is done close to the data source. Putting these processes closer to the actual devices where information is accessible improves delivery and decreases latency. Whereas a data center may be hundreds or thousands of miles away from end-users an edge data center could be in the next street, or at least in the same postal code. This is particularly useful for low latency applications, such as online gaming, currency transactions or any use case where near-instantaneous data transport is required.
Security Risks Of Edge Computing
1. Data Storage and Protection
Data acquired and processed at the edge does not have the same level of physical protection as data stored in more centralized locations. Vital information can be jeopardized by the removal of disk drives from an edge resource or transferring data to a memory stick. It might also be more challenging to provide reliable data backup due to restricted local resources.
2. Passwords and Authentication
Edge devices are frequently ignored by security-conscious operations personnel, and many have inadequate password policies. Hackers have devised advanced methods for breaching password schemes. A “botnet onslaught” targeted 5,000 IoT devices on a university campus in 2017, with 5,000 separate systems looking for weak passwords.
3. Data Sprawl
It becomes increasingly difficult to monitor when companies install more and more edge devices to oversee a larger range of operations. Devices may eventually overrun the edge’s limitations, causing bandwidth overuse and jeopardizing the security of numerous devices. IoT traffic increases delay as it expands, and when data is transferred unprocessed, it might jeopardize security.
What Are The Components of Edge Security?

Photo Credit: www.comodo.com
There are several key components to effective edge security:
-
Edge Device Security To Protect Endpoints
As part of the huge web of IoT devices, edge computing devices can take nearly any shape, from micro-data centers in faraway places to sensors, security cameras, cash registers, and routers that necessitate quick local processing. These endpoints may be found all over the place. As a result of the quick move to work-from-home models in response to the worldwide pandemic, IT departments now have to handle millions of scattered remote offices as well as BYOD devices ranging from laptops to smartphones to tablets.
The design of these edge devices frequently places a premium on utility and connection over security. Many don’t have a user interface (UI), which makes IT visibility more difficult. A device positioned at the network’s edge is similarly vulnerable to theft because it is generally tiny and physically exposed.
Some edge security methods, such as vulnerable VPN connections, might actually make you more exposed to zero-day threats. Effective edge device security, on the other hand, provides IT with a single pane of glass from which to control and monitor all devices. User authentication is automated on an ongoing basis, and access control measures are in place to ensure that users are who they claim to be before access to corporate data is given.
-
Cloud Security To Protect Data At The Edge
While the security of edge devices is crucial, the security of the cloud edge is critical. Despite the fact that the cloud remains the preferred destination for accumulating and analyzing data, the sheer volume of data created by internet-connected devices necessitates even more processing. Edge computing manages load by bringing processing and storage resources closer to the source of data, but moving data from the edge to the cloud—and especially from the cloud back to the edge—makes it highly vulnerable to assaults.
As enterprises transfer cloud capabilities across the WAN to users at the edge, sectors like healthcare and finance face greater challenges in protecting sensitive data that is subject to stringent compliance regulations. Important security elements like encryption are prioritized in cloud edge security, both for data stored locally and data in transit between the network core and edge computing devices.
-
Network Edge Security To Protect Internet Access
Users now demand direct internet access to cloud and SaaS apps as the network edge shifts. While increased connection benefits consumers, it also raises the potential of unwanted behavior migrating from the internet to the business network.
The internet becomes a reliable mechanism for connecting to company resources thanks to network edge security. This critical component delivers the security capabilities that businesses require to protect access without sacrificing performance. Web filtering, anti-malware, intrusion prevention systems (IPS), and next-generation firewalls that permit or prohibit traffic based on IP addresses are examples of network edge security solutions that are frequently embedded into an organization’s software-defined wide area network (SD-WAN).
How AKCP Solutions Help Companies Against Threats?
AKCPro Server: Centralized Monitoring Solutions bring edge security features into a single, unified security stack that includes:
-
Environmental Monitoring
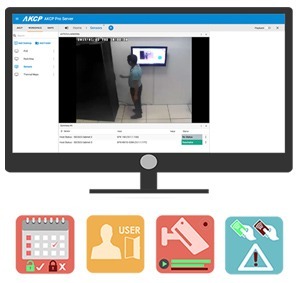
Access Monitoring Via AKCPro Server
Monitor all your temperature, humidity, airflow, water leak, and other environmental sensors. Configure rack maps to show the thermal properties of your computer cabinet, check the temperature at the top, middle, bottom, front, and rear, as well as temperature differentials.
-
Security Monitoring
Ensure that your facilities and critical infrastructure are secured. Door contact sensors, audible and visual alarms are configured and managed from your custom desktops in APS.
-
Power Monitoring
Monitor single-phase, three-phase, generators, and UPS battery backup power. AKCPro Server performs live Power Usage effectiveness (PUE) calculations so you have a complete overview of your power train and how adjustments in your data center directly impact your PUE.
-
Access Control
AKCPro Server is used to administer the access rights and schedules for all AKCP Door Control, Cabinet Control, and RFID Cabinet locks. Secure your assets, control access, and generate reports to give a complete audited trail of access.
-
Video Monitoring
Video feeds from Integrated ONVIF compatible IP cameras and cameras connected to AKCP securityProbe base units can be monitored and recorded in AKCPro Server. Synchronize sensor events with video in the playback window for an “eyes on” to any sensor events.
Reference Links:
https://www.sdxcentral.com/edge/definitions/what-is-edge-security-definition/
https://www.citrix.com/solutions/sd-wan/sd-wan-security/what-is-edge-security.html
https://internetofthingsagenda.techtarget.com/tip/Edge-computing-security-risks-and-how-to-overcome-them
https://datacenterfrontier.com/market-trends-lead-to-big-changes-for-it-management-systems/





