The infrastructure that supports the internet. It is made up of a huge variety of hardware and related devices. Let’s discuss the computing and non-computing resources that are essential components of data center .
What Is Data Center Infrastructure?
The physical components found inside a data center make up the infrastructure of a data center.Essentially, the IT hardware and supporting hardware, like cooling and air quality systems can be categorized as data center physical infrastructure.
The majority of people are familiar with the servers and data storage components that make up data center IT architecture, but there are other important non-computing components.
Data Center Facility Infrastructure Is More Than IT
Data center components for electricity and cooling are equally important to operations as IT-related technologies.
Maintaining uptime in a data center requires reliable power. The majority of data centers even include some kind of power failover and backup supply of electricity. Data centers typically connect to the local electrical grid.
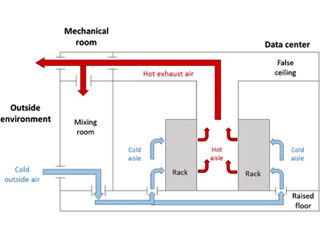
Additionally, the physical processes of data center operations frequently generate a lot of heat. Data centers must have cooling systems to control the temperature and humidity. There are other fire suppression technologies available in the unlikely event that cooling systems have a critical failure.
What Is Data Center Infrastructure Management?
Data center infrastructure management (DCIM) is a solution that mixes IT and Data Center Ops and may be used to achieve the best possible performance from a data center. Data center operations managers may better manage the physical components of the data center by using DCIM’s discovery, monitoring, reporting, and visualization tools.
Third party maintenance, like AKCP Monitoring Solutions can all be used in part or in full to maintain the infrastructure of a data center.
Types of Data Center Components
As we’ve established, core components of a data center are both the environmental infrastructure and the data center IT infrastructure.
Storage Infrastructure Data Center Components
Storage infrastructure includes things like network connected storage (NAS), directly attached storage (DAS), solid state drive (SSD) flash arrays, tape storage, etc. Manufacturers of storage devices include HPE, Dell EMC, NetApp, and IBM.
Server Infrastructure Data Center Components
Rack, blade, and tower servers that are utilized to store data and applications are referred to as server infrastructure. Servers can also be fully virtualized environments inside of actual machines, but since they are not physical infrastructure, they are not included in the data center components discussed in this article.
Network Infrastructure Data Center Components
Hardware like routers, switches, security devices, and firewalls make up network infrastructure. The connection and integration of the various data center hardware systems depend on these data center assets. Cisco, Brocade, Juniper, F5 Networks, and other well-known names are just a few.
List of Major Components A Data Center
Power
The majority of analysts view power as the data centers’ holy grail. This is necessary since many hosting services and computer systems require a steady and dependable power source.
For high uptime and guaranteed server performance, every data center needs a backup or redundant power supply in addition to the primary source. It couldn’t ever operate at peak efficiency without a consistent power source.
Because of this, data centers pay close attention to the power source and take steps to ensure that it is never disrupted.
Cooling Method
The cooling system for a data center is almost as crucial as the power supply.
It must be able to support the operation of the computer system, colocation servers, and networking hardware without causing any of them to overheat.
The information technology (IT) equipment in a data center can soon become hot if there aren’t adequate ventilation systems, cold or hot corridors, and raised floors. That would harm not only the system but also the data center’s ability to operate. All trustworthy data centers set up a suitable cooling system to keep the hardware system cool and the operations running smoothly.
Security
Security is the final aspect that must be there for a data center to run smoothly.
Sensitive data is stored on all of the servers and hardware in data centers. Well-maintained data centers employ constant monitoring, CCTV surveillance, biometric identification, and other security procedures to keep them safe.
Data center security includes both a virtual and a physical component. Choosing a location for data centers that have a very low risk of natural disasters like earthquakes, floods, and tornadoes is important for physical security.
Facility
The majority of the time, the locations where data centers are located are created particularly for that use. As a result, their ceilings may be taller than those of conventional structures. This is due to the necessity for more height for racks and overhead equipment. A data center may occasionally occupy just one level of a typical structure.
Equipment
For IT operations, data storage, and application development, every data center must have the necessary hardware and software. These could consist of servers, storage devices, network hardware including switches and routers, and firewalls among other information security components.
Back ups
As you can see from the foregoing, a data center must possess dependability and high uptime.
The data center’s fail-safe procedures for all of the data kept there are an important additional feature. This implies that every host of a data center must maintain and run a backup data center where all data is copied and kept. In case the primary point of operations has an unanticipated outage, datacenter providers must provide customers with a backup geo-diverse redundant data center facility.
Hardware
There must be a place to store all of a data center’s data. Computing units, data storage units like solid-state drives and hard disk drives, and other gear are responsible for this.
In order to make the best use of the facility’s space, racks are then built and mounted with the hardware. Typically, they extend all the way to the ceiling, leaving just enough space for cooling, circulation, and overhead cable systems.
Connectivity
Most data centers use the same strategies they use with power sources when it comes to being online. This indicates that several fiber connections to various internet service providers are frequently present in a single data center.
Making sure that the operations continue to function even if one of the internet providers goes down is the ultimate goal, just like with power. Always keep in mind that the data center’s dependability, safety, and scalability are paramount.
Growth Potential
The capacity of data centers to scale and expand in response to changing market demands is another crucial characteristic.
Colocation and dedicated server purchases are long-term investments. It must be able to adapt as your needs change as a long-term investment as your business grows. All data center providers must give customers the space they need to expand.
Types of Data Center Facilities
The evolution of data center infrastructure has caused the growth and classification of several different types of data center facilities.
- Enterprise Data Center Facilities
These are conventionally set up buildings that are solely owned and run by one company. These are often on-site, and an internal team is in charge of network monitoring, hardware upgrades, IT deployments, and maintenance.
- Colocation Data Centers
These include communal data centers where a company can lease space for servers and other technology. The advantage of colocation over internal data centers is that the colocation facility handles the building, power, HVAC, internet bandwidth, and physical security; you (the customer), however, are still responsible for providing and maintaining the gear.
- Managed Data Center
A corporation leases the physical infrastructure of a managed service data center, while a third-party managed service provider looks after the facilities and equipment. For more information about ParkView, our complete offering of managed services for the infrastructure of data centers, get in touch with Park Place Technologies right away.
- Cloud Data Center
Over the past few years, this kind of data center building has grown in popularity. A cloud data center is an off-premises location that your business may access over the internet, but you are not liable for the infrastructure’s upkeep.
Improve Efficiency With AKCP Monitoring Solutions
When it comes to future-proofing your data center, it makes sense to keep the leading provider of digital infrastructure support in your corner.
AKCPro Server
SPX+
Wireless Monitoring
Reference Links:
https://www.parkplacetechnologies.com/blog/data-center-infrastructure-components-facilities/