Computational Fluid Dynamics to Improve the Performance of Data Centers
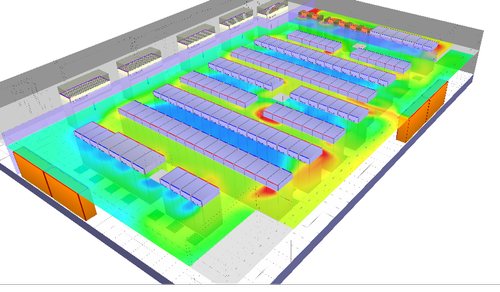
The global focus on sustainability has underlined the need to move toward more energy-efficient data center designs. These designs should provide the ideal combination of operational overhead reduction and reduced carbon footprints. The ultimate result is data center performance that is well optimized. When it comes to data center design, refit, and analysis to improve the efficiency and performance of legacy data centers, computational fluid dynamics (CFD) plays a critical role. It enables the operator to optimize racks, cabinets, cabling, and mechanical and engineering (M&E) equipment by simulating an infinite number of combinations.
What is Computational Fluid Dynamics Analysis?
CFD software provides a 3D model of a data center’s physical properties, including the location and performance characteristics of cooling units, IT equipment, power systems, and other critical data center components.
Computational Fluid Dynamics Revolutionizing the Modern Data Centers
Risk Mitigation With Strategic Computational Fluid Dynamics Analysis
- Perforated Floor / Ceiling Tiles
- Hot / Cold Aisle Containment
- Diversity In Of Heat Load Distribution On Each Server
- Underfloor / Overhead Plenum
- Cold Air Lobby
Design Airflow Analysis
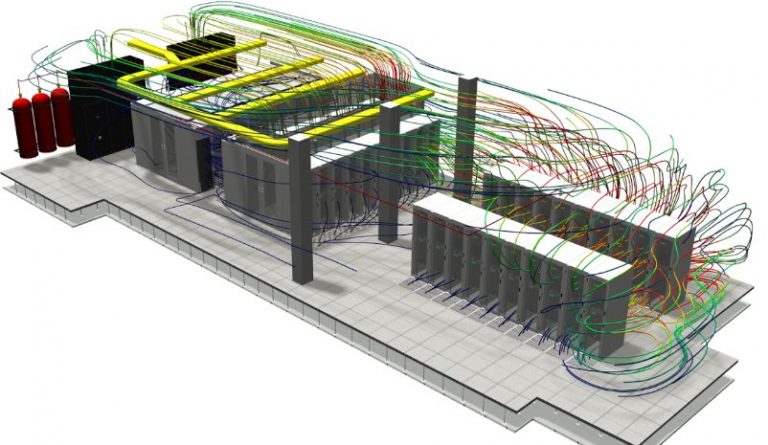
Damper Control for Supply Grilles
When all the supply plenum grilles are set at constant opening the air distribution can become uneven due to the pressure distribution in the supply plenum. CFD can help to identify the right opening area/control for each grille to ensure the most effective approach in achieving equal/requisite airflow through each grille.Server Configuration
Identify high-powered servers within the data hall and quantify where high cold airflow is supplied.Hot Spots
Day One Analysis
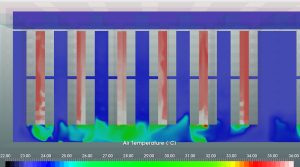 Multi-tenant data centers are common in today’s data centers. As a result, the data center may be planned to satisfy a given heat load need, but this demand will not be met for many days, weeks, or months after the data center is operational. So, after setting numerous units as ’empty,’ the analysis can be used to determine the most cost-effective strategy to cool the units that are functioning. During the early stages of operation, this helps predict the operation and operating expenses.
Multi-tenant data centers are common in today’s data centers. As a result, the data center may be planned to satisfy a given heat load need, but this demand will not be met for many days, weeks, or months after the data center is operational. So, after setting numerous units as ’empty,’ the analysis can be used to determine the most cost-effective strategy to cool the units that are functioning. During the early stages of operation, this helps predict the operation and operating expenses.Equipment Switchover Simulation
Leakage Analysis
AKCP Thermal Mapping
 AKCP is the world’s leading expert on professional sensor solutions. Our R&D centers specialize in SNMP-based networking and embedded device technology. AKCP is the first company to bring a workable, LoRa based wireless monitoring system and wireless tunnel for critical infrastructure to market. With features specifically tailored for the data center.
AKCP is the world’s leading expert on professional sensor solutions. Our R&D centers specialize in SNMP-based networking and embedded device technology. AKCP is the first company to bring a workable, LoRa based wireless monitoring system and wireless tunnel for critical infrastructure to market. With features specifically tailored for the data center.
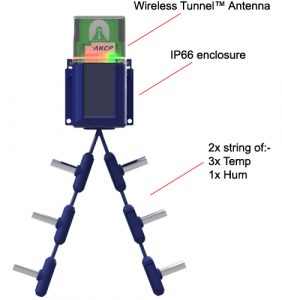
Monitor the temperature differential between the front and rear of your cabinet. Datacenter monitoring with thermal map sensors helps identify and eliminate hotspots in your cabinets by identifying areas where temperature differential between front and rear are too high. Wired and Wireless Thermal Map Sensor.
With three (3) temperature sensors at the front and three (3) at the rear, it monitors airflow intake and exhaust temperatures, as well as provides the temperature differential between the front and rear of the cabinet (ΔT).
Advantages Of Thermal Map Sensors
Obstructions Within The Cabinet
Cabling or other obstructions can impede the flow of air causing high-temperature differentials between the inlet and outlet temperatures. The cabinet analysis sensor with pressure differential can also help analyze airflow issues.
Server And Cooling Fan Failures
As fans age, or fail, the airflow over the IT equipment will lessen. This leads to higher temperature differentials between the front and rear.
Insufficient Pressure Differential to Pull Air Through The Cabinet
When there is an insufficient pressure differential between the front and rear of the cabinet, airflow will be less. The less cold air flowing through the cabinet, the higher the temperature differential front to rear will become.
Power Usage Effectiveness (PUE)
When the data is combined with the power consumption from the in-line power meter you can safely make adjustments in the data center cooling systems, without compromising your equipment, while instantly seeing the changes in your PUE numbers.
Conclusion
One of the major benefits of using CFD modeling and analysis is that it can quickly demonstrate how a containment solution will immediately reduce a data center’s energy cost and lower its environmental footprint.
Regardless of which type of containment is used, large energy savings can be achieved by optimizing the airflow and raising the supply temperature, while simultaneously eliminating hotspots. Additionally, containment improves the benefits and economic feasibility of other efficiency measures, such as digital scroll compressors, electronic commutation (EC) and variable speed drives, data center infrastructure management (DCIM) software, and building controls.
Containment also saves energy by isolating the cold supply air from the heated exhaust air, lowering running expenses. Yes, there is an upfront cost to install the containment solution, but with a potential return on investment (ROI) of 10-14 months, end-users will quickly see a return on their investment. Furthermore, they will save energy, reduce operating expenses (OPEX), and reduce carbon emissions to become more sustainable from that point on.
