Water Usage Effectiveness For Data Center Sustainability
The digital world has forced the expansion of data centers, with more edge, and hyper-scale data centers being built. According to Natural Resources Defense Council (NRDC), data centers used 91 billion kilowatt-hours (kWh). Their carbon emissions account for 200 million metric tons of carbon dioxide in a year. Keeping the data centers cool is one of the biggest energy hogs.
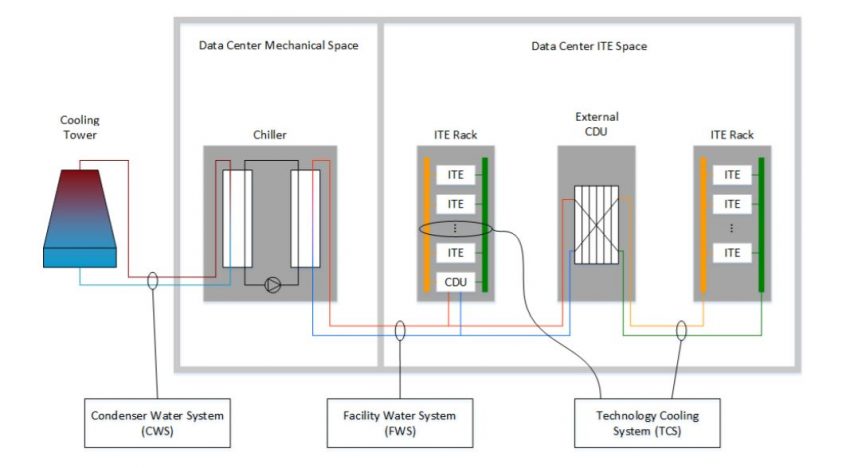
Data Center Sustainability
Data centers are now at the center of government and environmental advocates’ attention. They demand the administrators’ compliance with sustainable infrastructure. Data centers must be built with a commitment to innovative and sustainable strategies by using science-driven solutions. This includes green power, water conservation, recycling, and waste management.

- Power usage effectiveness (PUE)
- Data Center Energy Productivity (DCeP)
- Energy Reuse Effectiveness (ERE)
- Data Center Compute Efficiency (DCE)
- Carbon Emission Effectiveness (CUE)
- Water Usage Effectiveness (WUE)
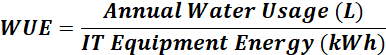
How to Achieve the Best WUE?
Recommended Cooling Strategies
1. Using Air-Cooler
- Get rid of the burden of water permit
- Water consumption/loss is reduced
- Reduced maintenance
- Requires huge space availability
- Additional cost
- Only applicable for selected data center environment
2. Using Water-Cooled Chiller
- Space-saving
- More economical to install
- Can use natural water
- Risk of contaminants getting into the cooling tower
- Extreme weather that evaporates and freezes the cooling tower
- Consistent monitoring of the water-level
- More complex maintenance
- Risk of water leakage
3. Using Adiabatic Coolers
- Addressing two issues in a single system
- High efficiency
- Cost-effective
- Risk of Legionella
The Importance of Monitoring
The efficiency of the cooling system
- The efficiency of each of the cooling compressors and pumps
- Leakages with the cooling system
- Reduce start/stop cycles
- Amount of water usage
ACKP Wireless Water Distribution Control
- 4x AA Batteries
- 5VDC or 12VDC powered
- LED indicators for power, status, and RSSI
- Optional DIN rail or pipe mounting
- Control direction of DC motors
- Dry contact input for status
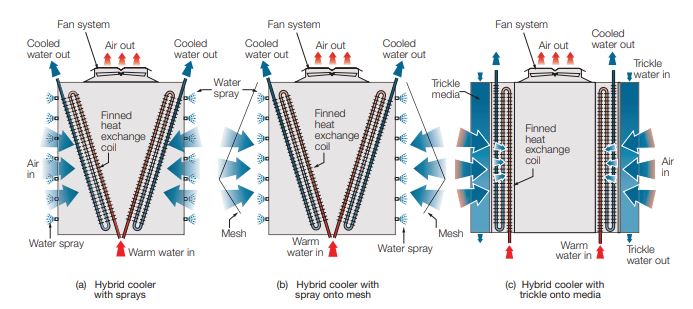
Wireless Tank Level Sensor
Monitor tanks of depths up to 20 meters. Often tanks are located in outdoor or difficult to cable areas. The WT-TDPS is battery powered or can be powered from a 5V DC or 12VDC source. Track fuel usage, graph the tank level, receive alerts when tank levels are critical. No more constraints on maximum cable lengths from the base unit
Sensor Features
- 4xAA Battery powered, with 10-year life*
- Tank mounting kit with cable gland
- IP66 rated enclosure
- Monitor all kinds of liquids and fuels.
Leak Detector

Ideal for detecting water leaks in hard-to-see areas, such as under-raised floors and false ceilings. The Locate Rope Water sensor will give you a precise location of the water leak so you can respond promptly to protect your enterprise resources from water damage.
This sensor comes fully assembled and includes the rope portion that is the water sensing cable, the non-sensing cable (from the rope to the sensing module), and the main sensing module. The sensing cable can be pre-ordered from a 10-foot minimum to any custom run length (in multiples of 10 feet) of up to 160 feet. The non-sensing cable comes in a standard 20-foot run length.
The specific location of water along the rope can be used to trigger alerts like e-mail, SMS, phone calls, and SNMP traps. The sensor has its own SNMP OID so that it can be monitored over the network using any Network Management System.
