IEEE 802.1x Authentication | What is IEEE 802.1x

What is IEEE 802.1x
What is IEEE 802.1x? It is a standard for the identification of devices. Deployed on IP LAN Networks, whether wired or wireless. It is an aid to securing your network and enhancing the security. It allows control of which devices are authenticated for access to the LAN.
Why is Authentication Important on Networks?
When your computer connects to another computer or service online, how do you know that it is really the computer you intended? Authentication will verify that the device being connected is what it claims to be. For example, when connecting to your online banking, you would want to authenticate that it is really is your bank server and not someone pretending to be it. On a LAN there are several different types of authentication used. PPP, EAP and 802.1x. To get a full understanding it is important to review what PPP and EAP are first.
PPP and EAP
PPP
Point – to – Point Protocol. It was commonly used in dial-up internet connections, and occasionally for DSL. It is a method to identify the modem on the connection. For example, the username and password used for connection are authenticated at the ISP and allow access to their network.
EAP
Extensible Authentication Protocol. It is a second layer of the PPP tunnel on a LAN. EAP defines the information and the format in which it should be provided. EAP is used in IEEE 802.1x and IEE 802.11 (WiFi) as the primary method of authentication. There are different types of EAP that can be used. Protected EAP (PEAP), Transported Layer Security (TLS) and Tunnelled TLS (TTLS).
PEAP
A popular and easy to implement EAP type. A username and password must be entered when connecting to the network.
TLS
This is one of the most secure options, but it is more difficult to implement and maintain. It uses an SSL certificate for both the Supplicant and Authentication Server validation. There are no username and passwords used. The Supplicant must have an SSL certificate file that can e provided to the Authentication Server for identification.
TTLS
An improved version of TLS, it does not require the Supplicant to have a pre-installed SSL certificate. This makes the management of the system easier.
EAP is encapsulated over IEEE 802, as defined in the IEEE 802.1x standards. This is called EAP over LAN or “EAPOL”. EAPOL communication is used between the Supplicant and the Authenticator. RADIUS protocol is used between the Authenticator and a RADIUS server.
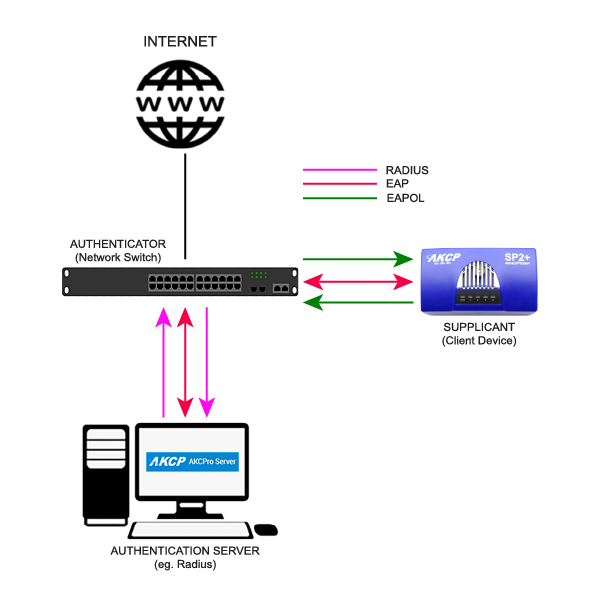
What is IEEE 802.1x architecture?
In 802.1x authentication, there are three main components.
- The Supplicant. This can also be called the client, or end-user. It is the machine that wishes to be authenticated and allowed access to the network.
- The Authenticator. This is a network access point (eg. WiFi Router) or switch. This is a device that sits between the Supplicant and the Authentication Server. It manages the traffic, acting as a proxy for the Supplicant. It can also restrict access to the Authentication Server.
- The Authentication Server is usually a RADIUS server. This decides whether the Supplicants request for full access to the network is valid.
In a wired LAN, the network switch receives packets from the Supplicant and forwards them. Before a switch will forward packets the device attached to that port must be authenticated. Once the device is disconnected or logged off, the port will be switched back to an unauthenticated state waiting for the next connection. They merely pass on the authentication information between the Supplicant and the Authentication Server with the actual authentication, checking of password and credentials being done on the Authentication Server. IEEE 802.1x supports multiple types of authentication. It may be a password, a hardware token, challenge and response question or digital certificates.
What is IEEE 802.1x Authentication Procedure
When a new device (Supplicant) connects to a LAN, the authentication procedure begins. It sends a request to the Authenticator, which is acting as a proxy for the

Supplicant. It will pass on the information, without giving the Supplicant access to the complete network. The Authenticator is acting as a filter, limiting the traffic that can get to the authentication server.
The Supplicant will initiate the procedure by sending an EAP message. Or, the Authenticator may send an EAP request to the Supplicant asking for its identity. Once the Authenticator has received the EAP response, the Authenticator will proxy this response and send it to the Authentication Server.
The Authentication Server will issue a challenge, requesting the Supplicant to prove their identity. Sometimes, if mutual authentication is being used, the Authentication Server will also send its own credentials proving its identity. This takes palace over RADIUS protocol between the Authentication Server and the Authenticator.
The Authenticator will forward this to the Supplicant. If mutual authentication is being employed, the Supplicant will also at this time check the Authentication Server credentials. It will then respond with its own credentials.
The Authentication Server will then either accept or reject the Supplicants request. If accepted, the Supplicant will have full access to the network through an authorized port on the Authenticator. Once the Supplicant disconnects or logs out, that port is closed and must be reauthenticated when a connection is made.
How to get an Authentication Server for IEEE 802.1x
The most popular authentication server is freeRADIUS. It is an open-source project for AAA servers. It is however for advanced IT system administrators. It is available for Linux, MAC OSX and Windows.
Windows Server includes an Internet Authentication Service (IAS) in Windows Server 2003. In Windows Server 2008 it is called the Network Policy Servers (NPS).
Setting up IEEE 802.1x Authentication
Now you understand what is IEEE 802.1x Authentication, and why it is important, you may want to deploy it on your corporate network. Below are the steps you will need to take.
- Setup your RADIUS server (Authentication Server)
- Configure the RADIUS server with the EAP settings for the EAP type you will use.
- Configure your access points (Authenticator), routers, switches etc with the RADIUS server details
- Configure the end devices (Supplicant) with the encryption settings
AKCP and IEEE 802.1x
Due to increasing concern over the security of networks, IEEE 802.1x authentication is becoming more prevalent. In order to keep up with the demands of IT professionals, AKCP is implementing IEEE 802.1x on our sensorProbe+ series of base units.





