Ghost servers are a pervasive problem in data centers. They can consume valuable resources and cause security risks. A ghost server is a server that is in the data center but no longer in use. Some may not even be registered in the data center management software. They are often forgotten about or left behind after being decommissioned. They can take up valuable space and resources without providing any value.
The accumulation of ghost servers in a data center can have consequences to the operations bottom line. They consume power, cooling, and other resources without providing any value. In turn, they drive up operating costs and reduce the efficiency of the data center. Additionally, ghost servers can create security risks if they are not managed. They may still be connected to the network and be accessed by unauthorized individuals.
In this article, we will discuss what ghost servers are, why they are a problem, and how to identify and prevent them in your data center. Addressing the issue of ghost servers can help ensure that your facility is running efficiently.
We will look at various methods for detecting ghost servers. This includes checking the physical inventory and using network scanning tools. As well as strategies for decommissioning unused servers to prevent them from becoming ghost servers. Following these guidelines can help keep your data center free of ghost servers.
The problem with ghost servers
If you have a data center with 2,500 servers, 10% of those are likely ghost servers. These ghost servers can be costly, consume energy, and require space, cooling, cabling, and maintenance. For example, if you have 250 ghost servers that each consume 175 watts at idle, they could cost you $64,000 in energy bills for a year. Identifying and eliminating ghost servers can help reduce energy consumption. As well as improve efficiency in your data center.
Ghost servers are caused by a variety of reasons, including the following.
- Deployment of new hardware can cause older servers to be left behind without being properly decommissioned. This can result in the older servers remaining idle and still using power.
- When workloads are moved to the cloud, older servers may be left behind and continue to use power. These servers may be forgotten about or considered a low priority, resulting in them remaining idle.
- Excess capacity may be deployed in anticipation of the need to quickly roll out a new service. This can result in idle servers being powered on and ready but never actually being used.
- Lack of tools and information can make it difficult to identify potential ghost servers. This can result in ghost servers remaining unnoticed and continuing to use resources.
Identifying ghost servers in your data center
Here are four steps to identify ghost servers in your data center:
- Shine a light on the ghosts. Use an energy management solution to collect and monitor power and temperature data throughout the data center. This will provide visibility into the activity levels and help identify ghost servers.
- Match assets to demand. Use the collected data to better understand workloads and service levels in the data center. This can help identify servers that can be powered down during periods of lower activity. As well as adjust workloads to offload servers operating close to their maximums.
- Adjust the ambient temperature. Increasing the ambient temperature in the data center can reduce demand on the cooling systems and result in energy savings. Yet, this decision should be based on the specific equipment in the data center. As well as its ability to operate at higher temperatures.
- Automate threshold management. Use an energy management solution to monitor and adjust temperature and energy thresholds. This will help you avoid conditions that could lead to outages or other issues. It helps ensure that the data center operates optimally without risking equipment or data.
Ghost servers, also known as zombie servers, are servers that are deployed in data centers but are not being used for any useful function. These idle servers waste valuable space, energy, and money. Using intelligent rack PDUs and DCIM software allows operators to identify and remove ghost servers. This results in cost savings and more efficient use of resources. DCIM software also allows managers to track the impact of removing ghost servers in real-time. As well as make further improvements to their data centers.
Preventing ghost servers in your data center
Implementing an effective asset management system can help monitor server usage and workloads. Allowing data center managers to identify potential ghost servers and take action to prevent them. Shift workloads to other servers, repurpose underutilized servers or decommission them altogether.
Monitoring and analyzing energy usage and temperature data can also help identify ghost servers. It prevents the proliferation of this problem in your facility. By implementing a comprehensive energy management solution, data center managers can gain visibility into the power and thermal patterns. Allowing them to identify ghost servers and take action to prevent them.
Energy management solutions have been widely used in data centers to reduce energy waste by up to 40%. Here are some data centers that prove eliminating ghost servers are crucial for your facility.
- EMC tested a new technology to help manage the power used by their Atmos cloud storage. This technology allows them to monitor how many servers they can fit in each rack and how much energy they use. This technology also helps EMC save energy by reducing the amount of power used by servers when they are not being used. EMC was able to reduce the amount of power used by these idle servers from 50% to 15%.
- Korea Telecom did a test for a new energy management solution with the goal of maximizing the number of servers in its data center. The test showed that power consumption could be reduced by 15% with the new conservation policies. Data center workers found servers that were not being used very much. By turning them into lower-power mode, they were able to save $2,000 per year per rack.
- BMW found that using virtualization and energy management technologies together can help save energy. Tests showed that they could save about 18% in power.
Eliminate ghost servers with AKCP
AKCP monitoring solution is here to help you ghost servers in your facility. Data center managers can collect and monitor real-time server inlet temperatures and power consumption data. This information can be used to identify ghost servers. As well as accurately define the optimal number of computing and storage servers.
Once ghost servers have been identified, the AKCP monitoring solution can be used to automatically power down. As well as repurpose the servers during periods of lower activity. This can help reduce energy consumption and improve efficiency in the data center.
AKCP monitoring solution can monitor airflow throughout the data center and at computer-area air handlers. This can help identify hotspots and optimize rack densities for more energy-efficient cooling.
AKCP monitoring solutions can provide data center managers with the necessary visibility and tools to identify and eliminate ghost servers. Improving efficiency and reducing energy consumption in the data center. Visit our website at akcp.com to learn more.
Photo credit: https://www.akcp.com/akcp-products/akcpro-server/
- AKCPro Server Central Monitoring Software
AKCPro Server is our world-class central monitoring and management software. Suitable for a wide range of monitoring applications. Free to use for all AKCP devices. Monitor your infrastructure over a wide geographic area, whether a single building or a remote site. Integrate third-party devices with Modbus, SNMP, and ONVIF-compatible IP cameras.
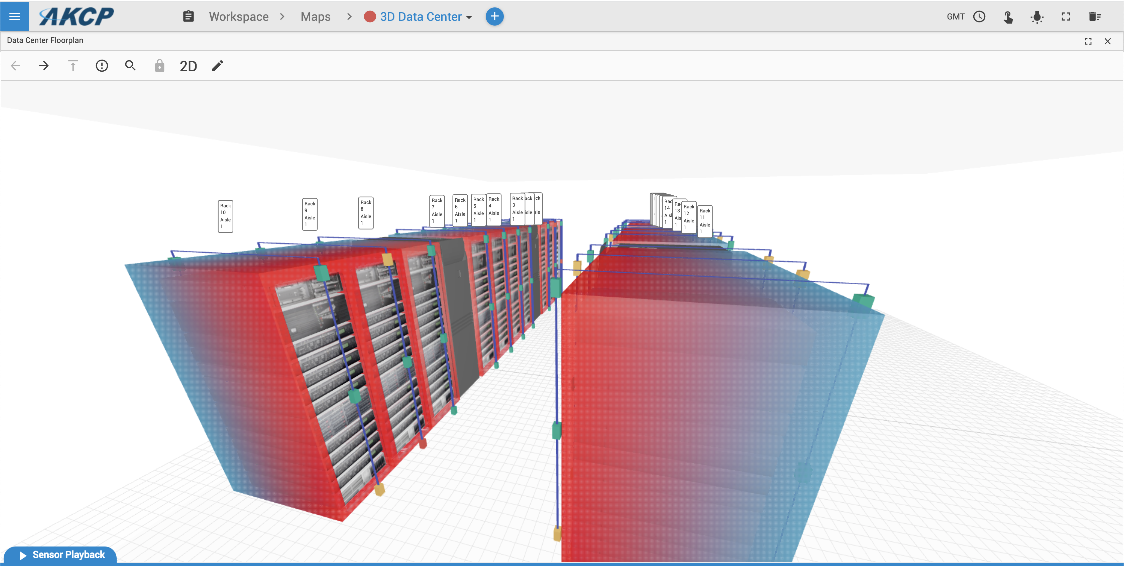
AKCPro Server 3D Heatmaps with Wireless Tunnel thermal map sensors
Conclusion
In conclusion, ghost servers consume energy and resources without providing useful functions. They are common in all data center facilities. The presence of ghost servers can be costly. They waste energy and money, reducing space and cooling capacity. Data center managers can use outlet-metered intelligent rack PDUs and DCIM software to collect and analyze power consumption data. As well as locate ghost servers and create change management requests to decommission them. Using these tools, data center managers can improve efficiency and reduce energy waste in their data centers.





