Aspects That Are Changing the Game
-
Aging Population
-
Lack of Skilled Workers
-
Regulatory Requirements
-
Real Estate Prices are Increasing
-
Demand is Increasing
What is a “Modular” Data Center?
3 Types of Modular Data Center
-
The ISO Container
-
Skid-Mounted
-
Enclosure
2 Types of Modular Data Center Enclosures
-
-
-
All-in-One Enclosure
-
-
-
-
- Bespoke Enclosure
-
-
Fully prefabricated indicates the data center is made up of modular enclosures. This should be tested, including IT, power, and cooling.
-
Semi-prefabricated is those are manufactured and tested off-site. This is before transporting them for installation in a stick-built data center.
-
A data center that is self-contained and supplied ready to use is known as an all-in-one. Making the appropriate network and power connections is all that is required.
Modular Data Centers’ Advantages
-
Shorter Time to Completion
The time it takes to complete a project is essential since it reflects the time it takes to generate money. Once the requirements of a data center are established, it will rush to finish the structure to generate profit. Most data centers take 18 to 24 months of construction. However, constructing a modular data center can save you up to 30% on construction time. It can also avoid delays caused by bad weather, equipment breakdowns, and other issues.
-
Cost Savings
Modular data centers are 30% less expensive than stick-built data centers. In reality, acquiring a modular data center is like purchasing a piece of custom-built equipment. Because the components needed are known ahead of time. The cost of assembly is fixed, and you just pay one price for the final product. Though modular data center suppliers include installation in their cost estimations. One of the most appealing elements of becoming modular for many businesses is the ability to control expenses.
-
Easier to Install
With the scarcity of construction personnel, modular construction eliminates the need for employees. You won’t have to worry about pulling wire or integrating electrical and mechanical components on-site. The enclosure is done at the factory and assured by established procedures. All work is done to set requirements, and everything is tested before delivery. This not only means a complete plug-and-play data center that is ready to install, but it also means a safer job site.
-
Compact Architecture
Although real estate is expensive, a modular data center requires a modest footprint. The data center may be put up in a parking lot or next to a building if you choose an outdoor installation, and it will take up very little area. This not only gives you more options, but it may also save you money, especially in high-rent areas like New York City or Chicago.
-
Totally Customizable
While the components are pre-assembled, the final design is entirely up to you. You have a variety of alternatives in terms of rack location, power capacity, cooling, and so on, depending on the form factor. Prior to production, all wiring, power, cooling, and other operating parameters are specified. Because you can add more systems and capacity, system expansion is quite simple. You also don’t have to overbuild to handle future expansion, unlike stick-built data centers.
-
Greater Dependability
During the manufacturing and assembly process, every component placed in a modular data center is verified. This indicates there’s a lower chance of failure.
-
Lower PUE
Because of the modular unit’s compact size and the fact that the components are matched, PUE is lower than in brick-and-mortar data centers.
-
Easy to Protect
A modular data center is simpler to secure. Since it is smaller and self-contained, especially if it’s behind a secure barrier with video surveillance.
In a nutshell, modular data centers are appropriate for any application that would benefit from a traditional data center. Modular data centers will continue to prove to be a cost-effective and long-lasting solution as demand for additional data center adaptability grows with the introduction of private and hybrid cloud computing and edge computing.
AKCP Wireless Monitoring Solution
Prefabricated modular data centers are built to suit business-specific requirements and fit in a right-sized secure infrastructure. We can provide complete data center solutions with our diverse product portfolio and established project services.
AKCP solution’s expertise spans sales, from project services, and engineering, to the complexity of creating data centers in its continuously changing needs. AKCP ensures that the monitoring is designed to your exact requirements, with the lowest cost, the most flexibility, and scalability.
Our wireless monitoring solutions integrate power, thermal management, and other environmental solutions, all of which are pre-integrated and calibrated, minimizing deployment time and on-site work. Future-proof your data center with the support of the industry leaders.
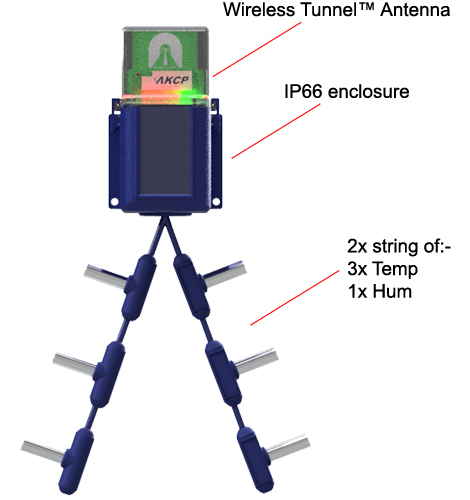
With the wide range of wireless environmental sensors on the market. Most are not for modular data centers. AKCP has over 30 years of experience in providing professional sensor solutions. They took on the challenge of developing wireless environmental sensors that were tailored specifically for monitoring critical infrastructure. They have brought to market the world’s first LoRa based monitoring system with features specifically for the data center. The Wireless Tunnel is a holistic approach to wireless sensor monitoring. It comprises of:
- Wireless Tunnel Sensors
- Wireless Tunnel Gateway-Server
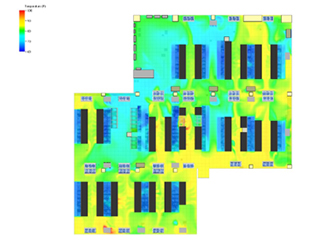
Wireless Thermal Maps
- AKCPro Server
Wireless Sensors
Wireless Thermal Maps give temperature and humidity values for the front and rear, top-middle-bottom of the server cabinet as well as the front to rear differential temperature readings (ΔT).
Wireless Cabinet Analysis Sensor combines cabinet thermal maps with front and rear differential air pressure (ΔP), suitable for data centers using hot and cold aisle containment. All of these environmental sensors and more are available as part of the Wireless Tunnel system.
Wireless Tunnel Gateway
The sensors require a gateway to communicate with. The Wireless Tunnel Gateway collects and stores data from up to 30 environmental sensors. In small installations, the Gateway is used as a standalone monitoring system without the need for a cloud server or internet connection. The embedded user interface of the server provides customizable desktops, mapping, and graphing. Alerts are sent via SMS, E-mail, and SNMP Traps.
AKCPro Server
For larger installations with multiple gateways, a centralized monitoring platform is used to combine the data from all gateways. The Wireless Tunnel Server is a central management platform, AKCPro Server. The server software can be run in-house on your own server or hosted in the cloud. It is a Data Center Infrastructure Management (DCIM) platform with close integration to AKCP environmental sensors.
Reference Links:
https://www.datacenterexperts.com/resources/white-papers/modular-containerized-datacenters/165-data-center-knowledge-guide-to-modular-data-centers.html
https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8651297
https://www.rittaltic.es/KNOW-HOW-FILES/Catalogos/Modular_data_centres_in_containers_en.pdf
https://www.upsite.com/blog/the-4-delta-ts-of-data-center-cooling-what-youre-missing/